🚀 New Models & AI Tools in AITHYRA Chat
We’ve added powerful new AI models and tools to our AITHYRA platform! This guide covers everything you need to know about the latest models, when to use them, and how to get started with our AI-powered tools.
⚠️ Important: VPN Compatibility
Note: If you are connected to CeMM VPN, AITHYRA Chat will not work. Please disconnect from VPN before accessing https://chat.aithyra.at
🤖 New AI Models
OpenAI Models
GPT-5.2 Chat (latest)
General-purpose flagship chat model for professional knowledge work—fast, reliable, and strong at everyday writing, analysis, summarization, and coding help.
| Context Window | Up to 400,000 tokens |
| Max Output | 128,000 tokens |
| Knowledge Cutoff | August 31, 2025 |
| Best For | Drafting, summarizing, Q&A, routine coding |
💡 When to use: Choose this model when latency matters and the task is “normal difficulty.” Best for everyday work without the extra cost of thinking modes.
GPT-5.2 Thinking (High) & GPT-5.2 Thinking (XHigh)
Deep-reasoning variants of GPT-5.2 for complex problem solving, high-stakes analysis, and multi-step tasks where correctness matters more than speed.
| GDPval Score | 70.9% wins/ties vs industry professionals |
| ARC-AGI-2 | 52.9% (abstract reasoning) |
| AIME 2025 | 100% (math without tools) |
| Vision | Strongest vision model—half the error rate on charts/UI |
Thinking (High)
Default deep reasoning setting. Use for: tricky debugging, reasoning over messy requirements, complex data interpretation, compliance-sensitive writing.
Thinking (XHigh)
Maximum reasoning depth for hardest tasks. Use for: deep planning, difficult math proofs, multi-file refactors with edge cases. Higher latency & cost.
GPT Image 1.5
Image generation model for creating and editing images from prompts. Best for marketing graphics, concept mockups, internal documentation visuals, and rapid creative iteration.
Google Models
⭐ Gemini 3 Flash (New Default Model)
Fast, cost-efficient, multimodal model designed for high-frequency workloads. This model has been set as the standard default for users who haven’t configured their own preference.
| Context Window | ~1,000,000+ tokens |
| Max Output | 65,536 tokens |
| SWE-bench Verified | 78% (coding benchmark) |
| Multimodal | Text, image, video, audio, PDF |
| Efficiency | ~30% fewer tokens than 2.5 Pro on typical tasks |
💰 Why it’s the default: Best combination of low cost ($0.50/1M input, $3/1M output), strong performance, and broad multimodal support. Ideal for most everyday tasks.
Mistral Models
Mistral Large 3
High-quality general-purpose text model suitable for drafting, summarization, analysis, and coding assistance. Good choice when you want strong results while diversifying away from single-vendor dependence.
Devstral2 (Local Coding Model)
Local/on-prem coding model optimized for software development tasks where data residency, privacy, or offline use is required. Best for code generation, refactoring, and quick IDE-style assistance when cloud models are not permitted.
Anthropic
🏆 Claude Opus 4.5
Premium, highest-accuracy coding model for complex engineering tasks (multi-file refactors, difficult bug fixes, large legacy codebases).
| SWE-bench Verified | 80.9% (highest among all models) |
| Best For | Production-critical code, hard bugs, security-sensitive refactors |
| Characteristics | Highest consistency, lowest error rates on enterprise legacy code |
⚠️ Cost Warning: This is our most expensive model. Use only for production-critical code changes, hard bugs, or security-sensitive refactors. For routine coding tasks, use Gemini 3 Flash or GPT-5.2 Chat instead.
📊 Quick Model Comparison
| Model | Best For | Context | Speed | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gemini 3 Flash | Default choice, multimodal, high-volume | ~1M | ⚡ Fast | 💚 Low |
| GPT-5.2 Chat | Quality writing, analysis, routine coding | 400k | ⚡ Fast | 🟡 Medium |
| GPT-5.2 Thinking | Complex reasoning, hard problems | 400k | 🐢 Slower | 🟡 Medium |
| Claude Opus 4.5 | Critical coding, legacy systems | — | 🐢 Slower | 🔴 High |
| Mistral Large 3 | General text, vendor diversity | — | ⚡ Fast | 💚 Low |
| Devstral2 | Private/offline coding | — | ⚡ Local | 💚 Local |
✨ AITHYRA Tools & Applications
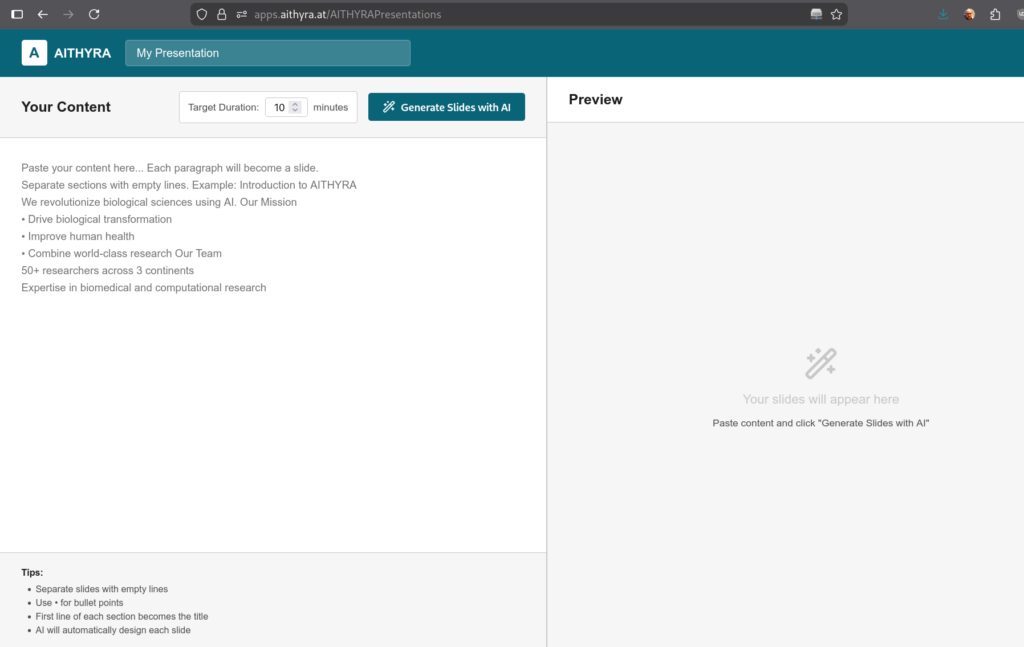
🎨 AITHYRA Presentations Tool
URL: https://apps.aithyra.at/AITHYRAPresentations
Our presentation app uses AI to create professional presentations within the AITHYRA PowerPoint templates from any content you enter. Simply provide your content, and the AI will generate a on-brand presentation automatically, and even suggesting prompts which let you generate images for your presentation.
With the exported file you continue to work in PowerPoint.
Features:
- Automatic slide generation from text input
- Uses official AITHYRA PowerPoint templates
- Smart content structuring and formatting
- Export-ready presentations
🔬 GPT Researcher
Research made easy! GPT Researcher automates the research process, helping you gather, analyze, and synthesize information from multiple sources quickly and efficiently.
💻 Coding Agents Setup
Use AI coding agents with your AITHYRA account to supercharge your development workflow. Here’s how to get started:
Step 1: Get Your API Token
First, you’ll need to generate an API key from AITHYRA Chat:
- Go to https://chat.aithyra.at
- Navigate to Settings → Account → API Keys
- If no key exists, click to create one
- Copy the API key (store it securely!)
API URL to use: https://chat.aithyra.at/api
⚠️ Model Compatibility for Coding Agents
Not all AI models support agent coding with tool use! Recommended models for coding agents:
- ✅ OpenAI models (GPT-5.2 series)
- ✅ Claude models (especially Opus 4.5 for complex tasks)
- ✅ Google models (Gemini 3 Flash)
- ✅ Mistral models
Other models may not support tool use and will not produce code results.
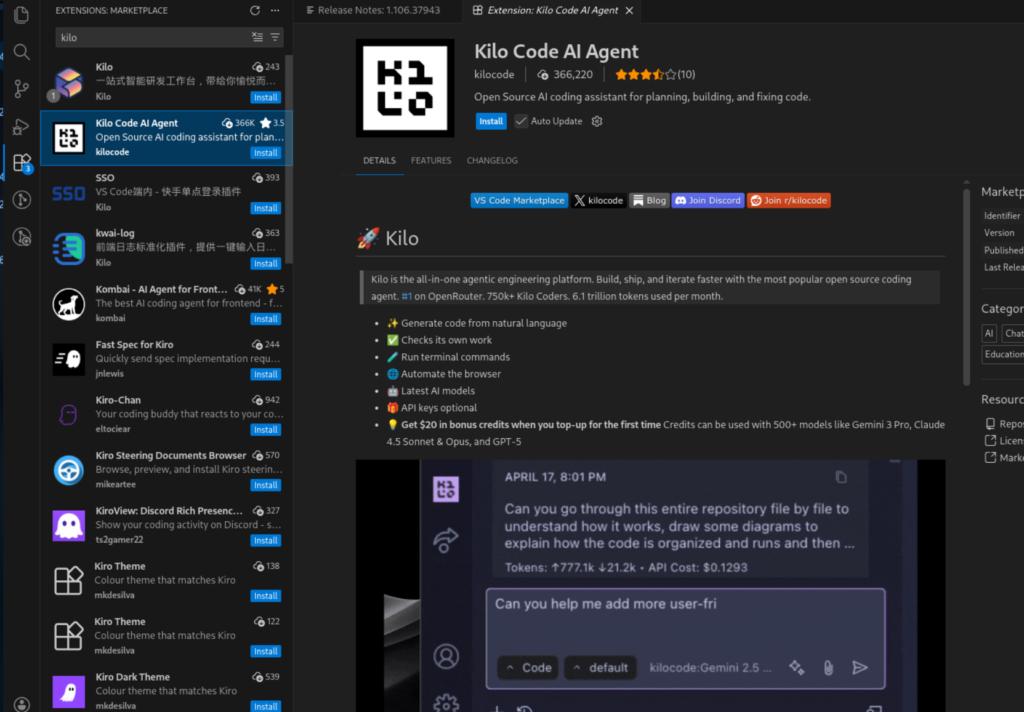
Option A: Kilo Code AI Agent (Visual Studio Code)
Website: https://kilo.ai
Kilo Code is a powerful VS Code extension that brings AI coding assistance directly into your editor.
Installation Steps:
1. Install the Extension
Open VS Code and search for “Kilo Code” in the Extensions marketplace, then install it.
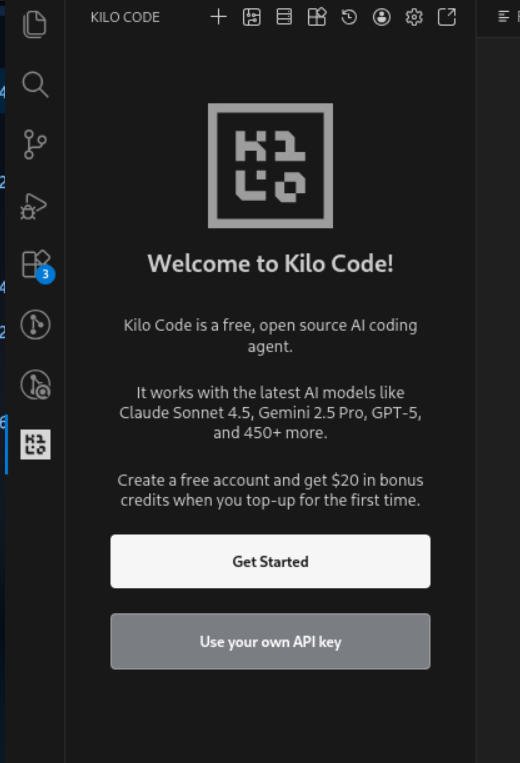
2. Configure Your API Key
Open Kilo Code settings and select “Use your own API Key”.
3. Set Up OpenAI Compatible Provider
Configure the connection with these settings:
- Provider: Select “OpenAI Compatible”
- Base URL:
https://chat.aithyra.at/api - API Key: Your key from AITHYRA Chat

Option B: ForgeCode (CLI-Based)
Website: https://forgecode.dev
ForgeCode is a command-line AI coding assistant for developers who prefer terminal-based workflows.
Prerequisites:
Node.js must be installed on your system. Download from: https://nodejs.org/en/download
Setup Steps:
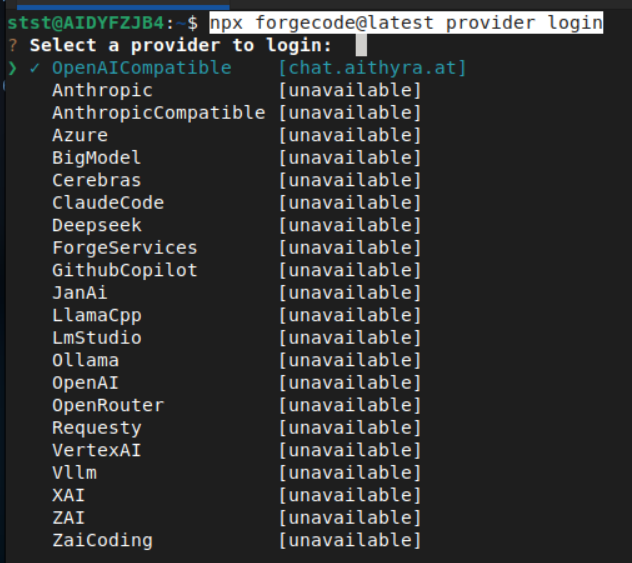
1. Run the Login Command
npx forgecode@latest provider login2. Select OpenAI Compatible Provider
When prompted, choose “OpenAICompatible” from the list.
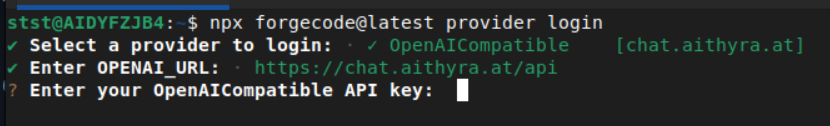
3. Enter Your Credentials
- URL:
https://chat.aithyra.at/api - API Key: Your key from AITHYRA Chat
4. Set as Active Provider
Select AITHYRA as your active provider when prompted.
5. Start Coding!
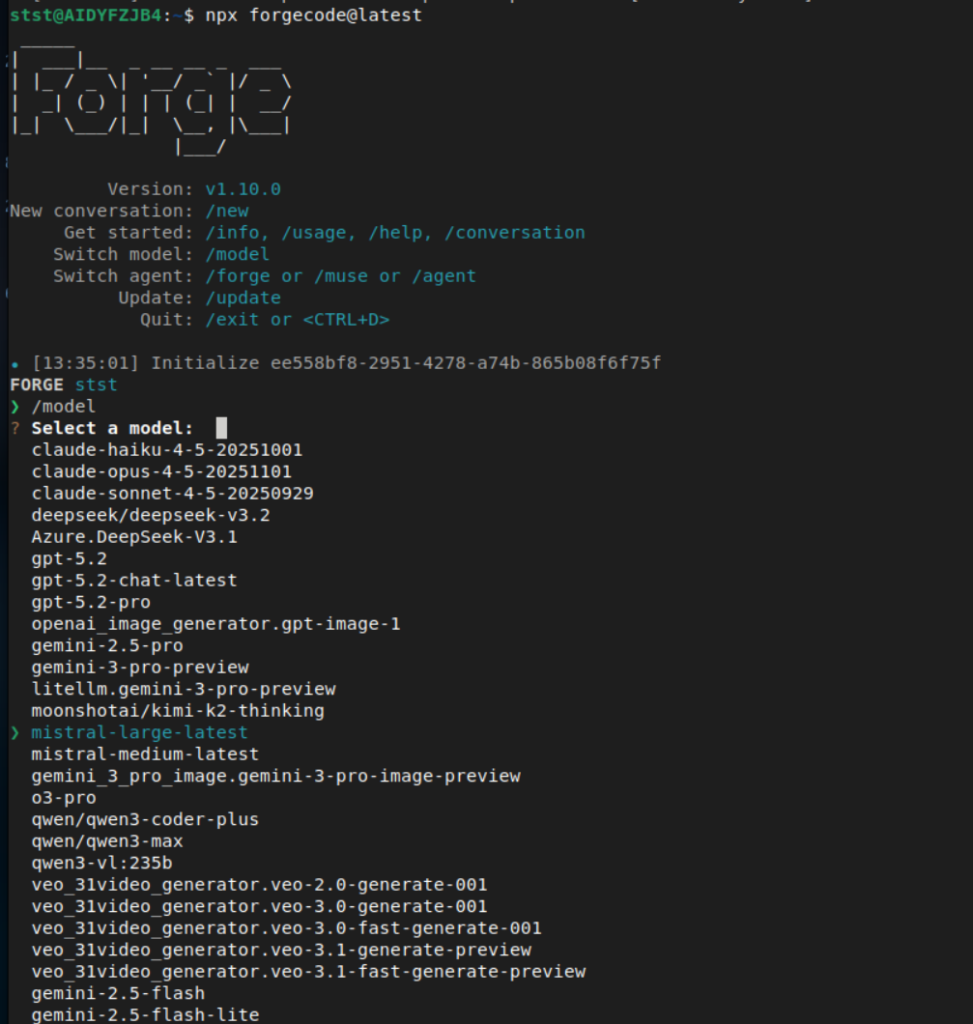
Launch ForgeCode:
npx forgecode@latest6. Select Your Model
Use the /model command to choose which AI model to use for coding:
❓ Need Help?
If you encounter any issues or have questions about using AITHYRA tools:
- Check that you’re not connected to CeMM VPN
- Ensure your API key is correctly copied (no extra spaces)
- Try a different model if one isn’t working with your coding agent
- Contact the IT team for further assistance